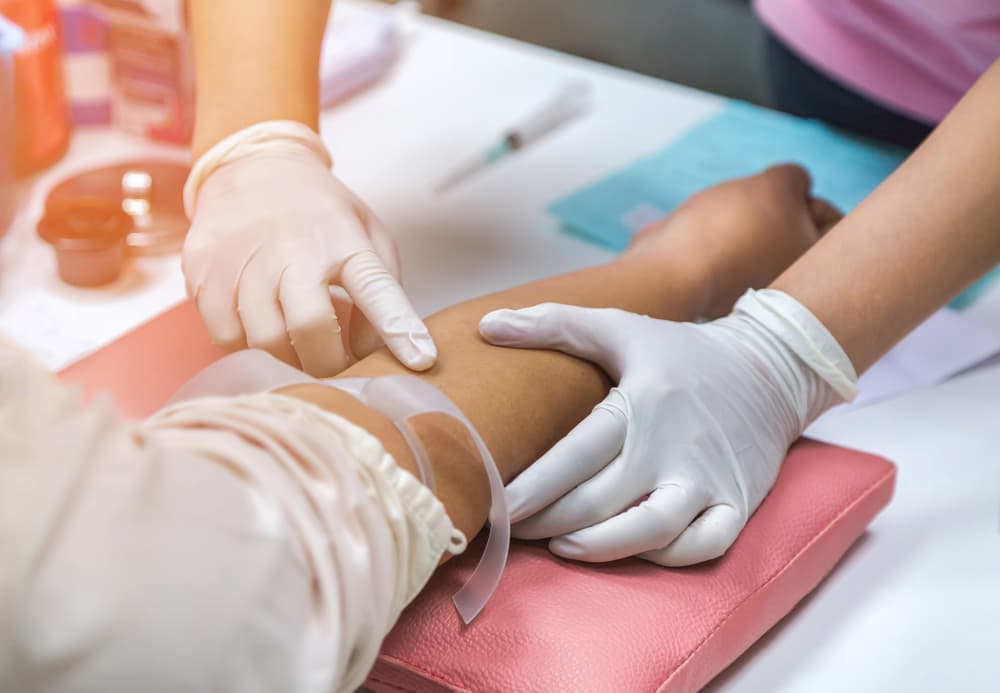
 It is normal to have some bruising after having your blood drawn. A bruise occurs when a blood vessel is damaged and blood escapes into the tissue under your skin. The pooling of blood causes a discoloration that is usually darker than the surrounding skin. Blood collects in the capillaries and leaks out slowly to cause the characteristic black-and-blue (or purple) mark. A bruise may also form if medical professionals fail to apply enough pressure to a needle when withdrawing it from a vein. This guide discusses why bruises appear after blood extraction and how to reduce the chance of bruising.
It is normal to have some bruising after having your blood drawn. A bruise occurs when a blood vessel is damaged and blood escapes into the tissue under your skin. The pooling of blood causes a discoloration that is usually darker than the surrounding skin. Blood collects in the capillaries and leaks out slowly to cause the characteristic black-and-blue (or purple) mark. A bruise may also form if medical professionals fail to apply enough pressure to a needle when withdrawing it from a vein. This guide discusses why bruises appear after blood extraction and how to reduce the chance of bruising.
Reasons Why Bruising Occurs After a Blood Draw
During blood drawing, a phlebotomist inserts a small hollow needle into the vein in your arm to remove a blood sample. This temporarily damages the blood vessel wall lining, causing blood from the damaged vein to settle under the skin. Some causes of bruising include:- Vitamin C and Vitamin K deficiency
- A history of alcoholism and liver damage
- Damaged blood vessels
- Medical conditions such as hemophilia, Cushing syndrome, thrombocytopenia, von Willebrand disease, and kidney or liver disease
- Small and hard to find veins
- Lack of enough pressure after the blood draw
- Consumption of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like naproxen and ibuprofen or anticoagulants like aspirin, clopidogrel, or warfarin.
How to Prevent Bruising After a Blood Draw
While some bruising during blood donation or blood tests is normal after blood draws, there are ways to reduce it. However, it is worth noting that different people tend to bruise more easily than others. If you are scheduled to have your blood drawn, you can follow these simple steps to avoid bruising:- Request a small butterfly needle for the procedure. These needles are more gentle and less likely to cause bruising than larger ones; WHO recommends butterfly or 22-gauge needles from drawing blood in the elderly.
- Apply firm pressure with your fingers after blood drawing and leave the bandage intact for at least six hours.
- Avoid wearing tight clothing as tight clothes can prevent proper blood flow and constrict blood vessels, increasing the risk for bruising.
- Refrain from strenuous activities and lifting heavy objects for a few days. This will allow your body to recover from venipuncture without unnecessary strain.
- Avoid taking pain relief drugs such as aspirin or ibuprofen several days before having your blood drawn and 72 hours after. NSAIDs have a blood-thinning effect that causes excessive bleeding.
- Apply a cold press using an ice pack on the injected region for pain relief and elevate your arm to reduce discomfort and speed up the healing process.
When to See a Doctor
It is important to know when to consult your doctor if you are worried about bruising after a regular blood draw process. In a few cases, a bruise may indicate an underlying problem such as internal bleeding, blood clot, or blood disease that requires medical attention. You may need to see a doctor if you:- Experience large unexplainable bruises
- Suddenly, begin bruising after starting a new medication
- Have acute pain or inflammation at the blood draw area
- Develop a lump on or near the area where blood was drawn
- Have a history of excess bleeding during medical procedures such as surgery
- Have a family history of bleeding problems
Learn More About Phlebotomy at Allen School
Bruising after a blood draw is a common occurrence, and while bruising is normal, some individuals tend to bruise more easily than others. It is important to know how to prevent bruising after a blood draw and be aware of when it becomes a cause for concern. Ready to start learning more about phlebotomy in one of our programs? Working towards a new career? Contact the Allen School today! We are enrolling now for classes starting soon. We cannot wait for you to become part of the Allen School family. Visit www.allenschool.edu to learn more.Image Source: Soonthorn Wongsaita / Shutterstock
